
⚖️ Hague Apostille Services | Apostille Direct London
Apostille Direct London provides fast, reliable, and professional Hague Apostille services for all types of document legalisation.
Whether you need papers for business, education, immigration, or personal use abroad, our specialists ensure your UK documents are fully legalised and accepted in all Hague Convention member countries.
What Is a Hague Apostille?
A Hague Apostille is a certificate issued under the Hague Convention of 1961, confirming the authenticity of a public document’s signature, stamp, or seal.
It allows that document to be recognised internationally between member countries of the Convention.
Why You Need an Apostille Certificate
An apostille is required when you present UK-issued documents abroad for official purposes, such as:
-
Business transactions and contracts
-
Employment or visa applications
-
Education and university admissions
-
Marriage or family matters abroad
-
Powers of attorney and legal agreements
Without this authentication, your documents may not be accepted overseas.
Documents We Can Apostille
We assist with most categories of official and private documents, including:
-
Birth, marriage and death certificates
-
Academic degrees and transcripts
-
Police or criminal record checks
-
Business and corporate documents
-
Powers of attorney and notarial acts
How Our Hague Apostille Process Works
-
Submit Your Documents – Deliver them in person or by courier.
-
Authentication & Certification – Our team checks each document and obtains the apostille from the FCDO.
-
Secure Return Delivery – We return your apostilled documents ready for international use.
Why Choose Apostille Direct London?
-
⚡ Fast Turnaround: Most documents processed within 1–2 working days.
-
Expert Team: Handled by experienced notarial professionals.
-
Central Location: Room 102, 8 Duncannon Street, London WC2N 4JF (near Charing Cross).
-
Secure Handling: All documents managed with strict confidentiality.
History of the Apostille – from the 1961 Hague Convention to the E-Apostille Era
The Apostille Convention, established in 1961 by the Hague Conference on Private International Law (HCCH), revolutionised international legalisation by replacing multiple layers of consular certification with one unified certificate — the Apostille.
Before 1961, documents required repeated stamping by local authorities, foreign ministries and embassies. The Hague Convention streamlined this process, allowing a single apostille to be recognised among member countries.
The term “apostille” comes from the French word for a marginal note and serves as an international form of certification similar to notarisation.
1961 Hague Convention Summary
Establishment of the Apostille System
The Convention replaces traditional diplomatic legalisation with a standard certificate issued by a competent authority in the country of origin.
Purpose and Effect
It removes the need for embassy legalisation between member states and simplifies the recognition of legal documents across borders for business, education and personal matters.
Types of Documents Covered
-
Birth, Marriage and Death Certificates
-
Court Orders and Judicial Documents
-
Notarial Acts and Certified Academic Degrees
-
Administrative and Government Records
Application of the Convention
As of 1 January 2025, over 127 countries participate in the Apostille Convention, and the list continues to grow each year.
You can view the official HCCH status table here.
Countries Outside the Apostille Convention
Non-member countries require a longer legalisation chain:
the document is first certified by a UK notary or solicitor, then by the FCDO, and finally by the embassy or consulate of the destination country.
Example:
For use in the UAE, a UK document must be notarised → apostilled by the FCDO → legalised by the UAE Embassy in London.
Competent Authorities
Each member state appoints its own issuing authorities.
In the United Kingdom, the only competent authority is the Legalisation Office of the Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office (FCDO).
Other countries delegate authority to different bodies — for example, Hungary assigns court documents to the Ministry of Justice and notarial acts to the Chamber of Civil Law Notaries.
Apostille Fees
The cost of an apostille varies by country:
| Country | Approx. Fee | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| United Kingdom | £40 (paper) / £35 (e-Apostille) | FCDO official fees |
| France / Japan | Free of charge | No fee applied |
| Cayman Islands | $180 USD | Regular service |
| Cayman Islands (Fast) | $240 USD | Priority service |
| USA – Indiana | $0 | Birth certificates |
| USA – Connecticut | $40 | Non-adoption documents |
Apostille Formats and Verification
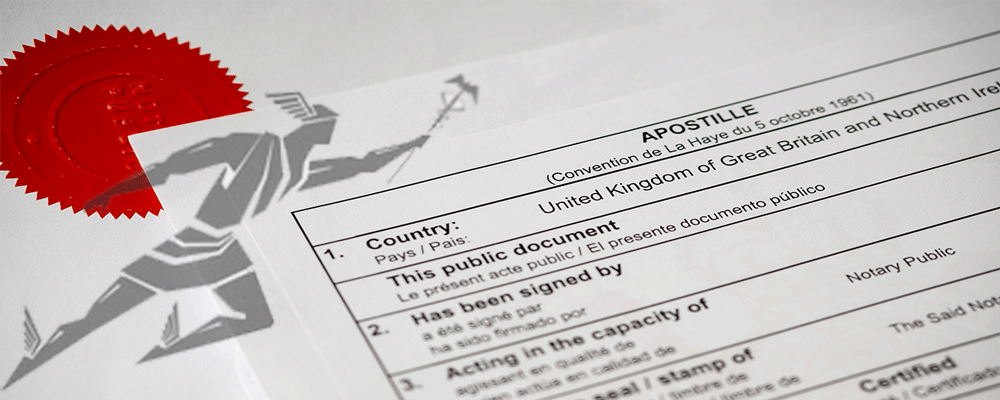
An apostille is a stamp or sheet attached to the document. It must contain the heading “Apostille (Convention de La Haye du 5 octobre 1961)” and ten numbered fields identifying the country, signatory, and issuing authority.
All competent authorities maintain a register of issued apostilles for public verification.
Validity and Expiry
While apostilles themselves do not expire, some countries require that the document be recent (e.g. less than six months old).
Always check the destination country’s requirements before submission.
General Benefits of the Apostille Convention
-
Eliminates the need for embassy legalisation
-
Simplifies international business and education processes
-
Enhances trust and efficiency in cross-border documentation
-
Reduces costs and delays in global transactions
Limitations of the Apostille Convention
An apostille confirms only the authenticity of a signature or seal — not the truth of the document’s content.
It cannot validate unaccredited academic certificates or fake documents.
To protect users, the HCCH recommends that apostilles carry the notice:
“This apostille only certifies the signature, the capacity of the signer, and the seal or stamp it bears. It does not certify the content of the document for which it was issued.”
E-Apostilles (Electronic Apostilles)
The Electronic Apostille Program (e-APP), launched in 2006 by the HCCH, modernised document authentication by allowing apostilles to be issued and verified digitally.
Key Features
-
Secure digital format with encryption and digital signatures
-
No paper handling or postal delays
-
Instant online verification via a unique identifier
Advantages
-
Speed: Same-day digital issuance
-
Cost-Efficiency: No printing or courier fees
-
Security: Reduced risk of tampering
-
Accessibility: Available worldwide through FCDO’s online portal
Adoption in the UK
The UK FCDO introduced E-Apostilles in 2022 after a pilot programme. In 2023 alone, the FCDO issued over 586,000 apostilles, with E-Apostille usage growing steadily among individuals and businesses.
Although widely accepted by most Hague Convention members, some foreign authorities still prefer traditional paper versions — always confirm before submission.
Contact Us for Expert Apostille Assistance
Our experienced team will guide you through the entire process — from document preparation to apostille issuance.




 Located directly opposite CHARING CROSS TRAIN STATION at: Room 102, 8 Duncannon Street, WC2N 4JF, London, United Kingdom
Located directly opposite CHARING CROSS TRAIN STATION at: Room 102, 8 Duncannon Street, WC2N 4JF, London, United Kingdom


